Managing asset versioning is vital for no-code app developers to ensure smooth updates, prevent crashes, and maintain control over changes. This guide highlights seven tools that simplify versioning for no-code projects, covering methods, ease of integration, pricing, and scalability.
Key Takeaways:
- AppInstitute: Ideal for quick updates in PWAs or controlled native app submissions, with pricing starting at $49/month.
- GitHub: Best for developers comfortable with Git-based workflows; free for small teams.
- Airtable: Combines database and file versioning, with a user-friendly interface; free and paid plans available.
- Supabase: Offers database and storage versioning; free for basic use, $10/month for advanced features.
- Firebase: Manages configuration and media versioning, integrates well with Google tools; free and pay-as-you-go options.
- Cloudinary: Focuses on media asset versioning and transformations; free with tiered paid plans.
- Xano: Backend versioning for databases and APIs, starting at $29/month.
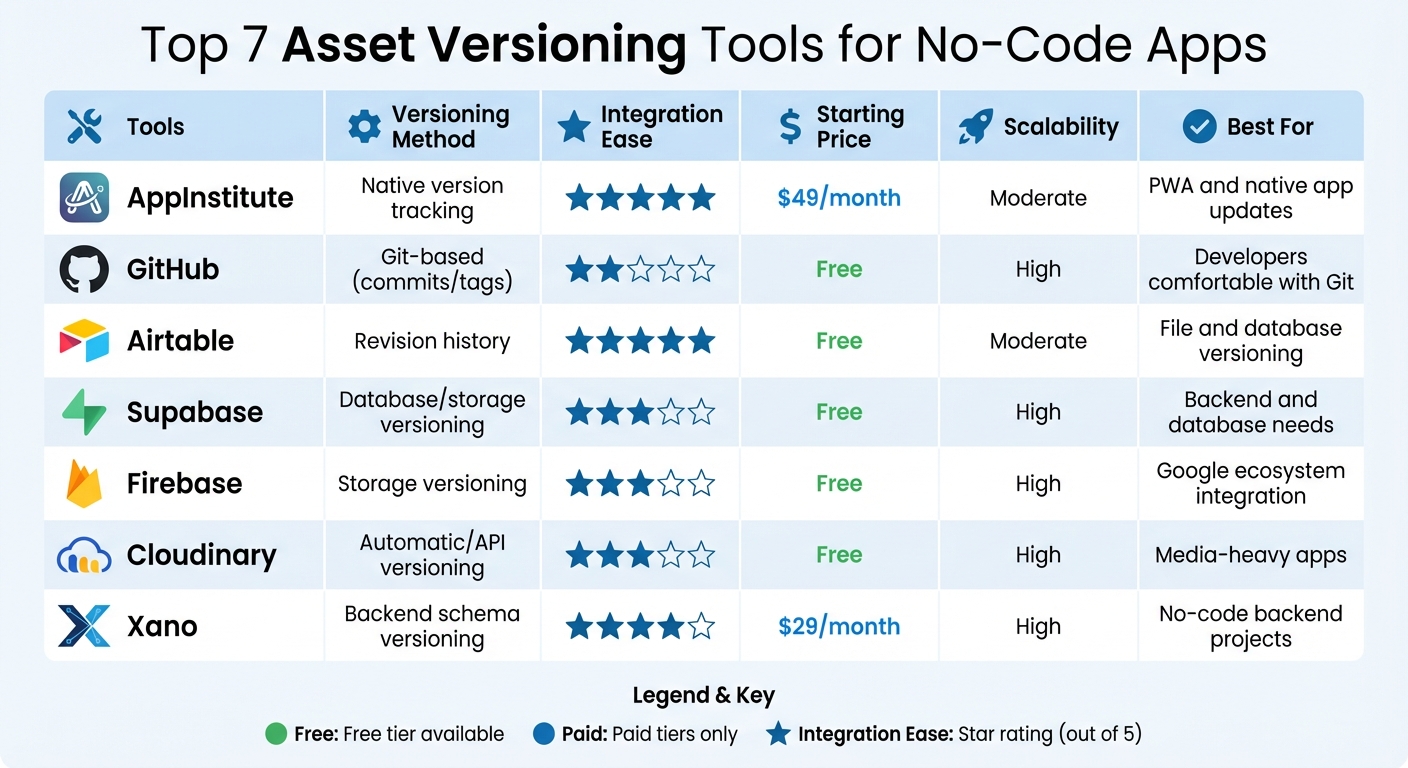
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Versioning Method | Integration Ease | Starting Price | Scalability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AppInstitute | Native version tracking | High | $49/month | Moderate | PWA and native app updates |
| GitHub | Git-based (commits/tags) | Low | Free | High | Developers |
| Airtable | Revision history | High | Free | Moderate | File and database versioning |
| Supabase | Database/storage versioning | Moderate | Free | High | Backend and database needs |
| Firebase | Storage versioning | Moderate | Free | High | Google ecosystem integration |
| Cloudinary | Automatic/API versioning | Moderate | Free | High | Media-heavy apps |
| Xano | Backend schema versioning | High | $29/month | High | No-code backend projects |
These tools cater to different needs, from comprehensive backend management to simple media asset updates. Choose based on your project’s complexity, team size, and required integrations.
Asset Versioning Tools Comparison for No-Code Apps
Why Asset Versioning Matters for App Performance
Keeping track of asset versions is crucial for ensuring your app runs smoothly and stays reliable. By managing and restoring asset versions and configurations, you create a safety net that shields your app from crashes and broken features. This becomes especially important when multiple team members collaborate on the same project. Asset versioning prevents accidental overwrites, helping maintain branch stability and ensuring a smoother workflow for everyone involved. It also plays a major role in how updates are numbered and managed.
“No-code platforms make it easy to build fast, but once your app grows past a few screens, asset versioning becomes essential. Keeping track of changes is the only way to scale without chaos.” Ian Naylor, Founder of AppInstitute
Speaking of numbering, Semantic Versioning is a widely-used system that uses a three-part format: Major.Minor.Patch. Each part signals the level of change in an update. Major updates introduce changes that might break compatibility, minor updates add features while maintaining stability, and patches focus on fixing bugs. This structured approach allows you to lock your app to specific, stable releases rather than risking crashes by pulling the “latest” updates.
“App versioning isn’t just about tracking changes – it’s a strategic tool that can drive your product’s success.” – Tope Longe, Product Analytics Expert, UXCam
Versioning doesn’t just stabilize releases; it also makes troubleshooting easier. By comparing performance metrics like load times or crash rates across different versions, you can quickly identify which release introduced a problem. Some developers even set up automated alerts to flag issues – like a 20% spike in crashes – so they can roll back problematic updates immediately. Additionally, certain tools prevent edits to released versions, reducing the risk of unstable updates.
“In our experience, versioning tools transform team workflows. When everyone knows exactly which asset changed (and why) collaboration stops being guesswork and becomes real productivity.” AppInstitute Team
Another critical aspect is cache management. As mentioned earlier, uploading a new version of an asset clears cached transformations, ensuring users get the latest content. While this process requires additional processing power, including version details (like a UNIX timestamp) in asset URLs can help. This approach ensures users bypass third-party caches at the browser, ISP, or corporate level, delivering fresh content without delay.
1. AppInstitute
AppInstitute takes a unique approach to managing asset versioning, setting it apart from traditional file-tracking systems. Whether you’re creating a Progressive Web App (PWA) or a native mobile app, the platform’s deployment architecture ensures updates are handled efficiently and systematically.
Versioning Methods
For PWAs, updates are instantaneous, meaning any asset changes go live immediately. On the other hand, native apps require a more controlled process. AppInstitute’s in-house team oversees compliance and submission to app stores, which typically takes between 1 to 5 days. To keep users informed, the platform provides real-time updates through tools like the Message Centre and News Ticker.
Simple Integration with No-Code Tools
The DIY AppBuilder’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes updating visuals a breeze. A dedicated Multimedia category simplifies rich media management with features such as a Video Directory for hosting video content and Radio Streaming for audio, music, and podcasts. Additionally, you can update content through HTML Content sections or by embedding external web resources directly into your app.
Pricing Plans
AppInstitute offers three pricing tiers to suit different needs:
- Instant Plan: $49/month, ideal for PWAs, includes push notifications and user management.
- App Stores Plan: $99/month, designed for native app submissions, includes unlimited resubmissions.
- App Stores Premium Plan: $149/month, adds tablet support, a dedicated account manager, and a free Hire A Pro service.
A 30-day free trial is available, allowing users to explore the platform’s features before committing.
Scalability for Growing Businesses
AppInstitute is built to grow with your business. For frequent asset updates, PWAs offer instant versioning without the delays associated with app store reviews. Native apps, meanwhile, provide optimized performance and seamless device integration. The platform also offers personalized 1-to-1 consultations to help you maximize its potential as your needs evolve.
2. GitHub
GitHub takes the basics of asset versioning and builds on them with advanced tools for managing commits and branches. Every change is recorded as a commit – a snapshot that creates a permanent log of your app’s assets and configurations. This means you always have precise control over updates and changes.
Let’s dive into GitHub’s core versioning approaches.
Versioning Methods
GitHub uses commits, branches, and semantic releases to track asset versions. Commits capture your progress at specific points in time. Branches allow you to create separate workspaces for testing new features without interfering with the main project. Meanwhile, semantic releases organize specific iterations of your app into bundles, making version management more structured.
For larger files like high-resolution images or videos, Git Large File Storage (Git LFS) is a handy tool. When preparing to publish, it’s a good idea to create releases as drafts first. This way, you can attach all necessary assets before finalizing the release, ensuring everything is in place.
But GitHub isn’t just about versioning – it also works seamlessly with no-code tools.
Integration Ease with No-Code Builders
Connecting GitHub to your no-code workflow is straightforward. Using a Remote SSH URL, you can commit changes, merge branches, and manage releases directly. For automation, GitHub Actions simplifies repetitive tasks and supports continuous delivery by automating processes whenever changes are pushed to a specific branch. And with Pull Requests, you can have team members review updates before merging them into the main branch.
Pricing Tiers
GitHub offers a range of pricing options. Free accounts are perfect for individual developers or small teams, while paid plans start at about $4 per user per month. These paid plans unlock extra features like advanced security tools and priority support. Since pricing depends on team size and feature requirements, it’s always a good idea to check GitHub’s website for the latest details.
Scalability Limits
As the most widely used version control platform worldwide, GitHub scales effortlessly to meet the needs of different projects. That said, integrating GitHub with no-code app builders can sometimes be tricky. Setting up APIs manually or using third-party tools like Zapier may add a layer of complexity compared to platforms with built-in versioning options. As your app grows in complexity and user traffic, you might need extra configuration to ensure smooth integration.
3. Airtable
Airtable blends the simplicity of spreadsheets with the power of databases, making it a versatile tool for asset versioning. It offers two key approaches: Managed Apps and Components, which focus on app structure, and Airtable Proofing, designed for managing digital assets like images and PDFs.
Versioning Methods
The Proofing feature turns attachment fields into versioned stacks. Each new upload increases the version number, creating a complete history of changes. Users can compare different versions, annotate files, and even track text changes in PDFs. Supported file types include images (JPG, PNG, GIF, TIFF) and documents (PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLS), with individual file sizes reaching up to 5GB.
For app development, Managed Apps rely on a Development Base for testing and building. Updates can then be pushed asynchronously to Child Bases, allowing users to control when changes are applied. Enterprise admins also have the ability to enforce updates across all bases if necessary.
Streamlined Integration with No-Code Tools
Airtable takes integrations a step further with its no-code-friendly approach. It offers native compatibility with platforms like Google Drive, Dropbox, Box, and Gmail. Its REST API, which uses JSON, ensures broad usability. Additionally, third-party tools like Zapier, Make, and Workato come with built-in Airtable connectors, linking your assets to thousands of apps without requiring any coding. The Airtable Sync feature ensures data stays updated across multiple bases and external tools.
“With Airtable, we can get metrics to leadership in minutes instead of days, which has transformed how we operate at scale.” – Sarah Sgarlato Pierini, Senior Research Program Manager
Pricing Options
Airtable offers a range of plans tailored to different needs:
- Free Plan: Includes 1,200 records per base and 1GB of attachments.
- Team Plan: Priced at $20 per user per month (billed annually), it increases limits to 50,000 records and 20GB of attachments.
- Business Plan: At $45 per user per month, this plan supports asset versioning through Proofing, with 125,000 records and 100GB of attachments.
- Enterprise Scale Plan: Offers custom pricing, Managed Apps, HyperDB for handling hundreds of millions of records, and 1,000GB of attachments.
Scalability and Performance
Airtable’s HyperDB infrastructure is built to handle up to 100 million records in a single table, serving over 500,000 organizations worldwide. It supports tens of thousands of simultaneous users. However, some users note a steep learning curve for advanced features and occasional performance issues when working with very large bases in browser mode. Despite these challenges, Airtable boasts a 4.5-star average rating across platforms like G2 Crowd, Capterra, and GetApp, based on more than 1,500 reviews.
4. Supabase

Supabase stands out as a developer-friendly platform, offering an efficient branching system that automatically sets up a testing environment for every new GitHub branch. This allows you to test database schemas, storage settings, and features without touching your production setup.
Versioning Methods
Supabase handles versioning through database migrations stored in a migrations directory, alongside versioned storage buckets and Edge Functions managed using a config.toml file. When branches are merged, updated assets are automatically deployed. Preview environments are populated using seed.sql files. The deployment process involves seven steps: Clone, Pull, Health, Configure, Migrate, Seed, and Deploy.
“Supabase branches create separate environments that spin off from your main project. You can use these branching environments to create and test changes like new configurations, database schemas, or features without affecting your production setup.” – Supabase Docs
This streamlined versioning system makes it easy to integrate with popular no-code platforms.
Integration Ease with No-Code Builders
Supabase seamlessly connects with no-code tools such as FlutterFlow, Bubble, Softr, and Noloco via its PostgreSQL integration. For Bubble.io, for instance, you can link your test branch to a Supabase test database and your live branch to the main database, ensuring a clear separation between environments. Its S3-compatible object store, combined with Row Level Security, enables efficient asset delivery through a global CDN that includes built-in image transformations. While some workflows currently require using the Supabase CLI for migration scripts, upcoming web-based tools aim to simplify this process.
Pricing Tiers
Supabase offers a flexible pricing structure, making it an affordable option for developers. Running a branch costs about $0.32 per day, which adds up to roughly $10 per month. A free plan is available to help you get started, and paid plans operate on a pay-as-you-go basis. For storage, Supabase supports unlimited scalability with three bucket types: Files, Analytics, and Vector.
“Supabase is great because it has everything. I don’t need a different solution for authentication, a different solution for database, or a different solution for storage.” – Yasser Elsaid, Founder of Chatbase
5. Firebase
Firebase operates on a unique model that separates static assets, configuration, and full-stack frameworks. It uses a dual-object system to distinguish content (Versions) from deployment pointers (Releases). This approach allows for precise control by keeping live content and testing configurations separate.
Versioning Methods
Each time you update Remote Config, Firebase generates a new versioned JSON template, making it easy to retrieve or roll back previous settings. The platform retains up to 300 versions of each template, automatically deleting the oldest ones as new ones are created. For web frameworks, App Hosting handles “Rollouts”, which can be triggered automatically through GitHub commits or manually via the Firebase Console.
Firebase offers two rollback options:
- Instant Rollback: Quickly restores a previous version using existing container images.
- Rebuild and Rollback: Reprocesses code with current configurations to ensure compatibility.
The platform also includes channel management tools. The “Live” channel is used for production, while the “Preview” channel supports temporary testing, with a default lifespan of 7 days (extendable to 30 days). Developers can clone specific versions across channels, hosting sites, or even separate Firebase projects, ensuring consistency between staging and production environments.
Integration with No-Code Builders
Firebase integrates seamlessly with no-code platforms like FlutterFlow and works effortlessly within Google’s ecosystem, making it a popular choice for tools such as AppSheet. Its Cloud Storage for Firebase manages user-generated content like photos and videos, using the same infrastructure that powers Spotify and Google Photos. The platform’s SDKs handle uploads and downloads efficiently, even on unreliable networks, thanks to resumable operations that conserve bandwidth.
For web applications, Firebase App Hosting offers built-in GitHub integration, enabling developers to trigger new rollouts with a simple git commit. Additionally, the Firebase Console provides a graphical interface for tasks like rollbacks, template editing, and viewing release history – no need for CLI access. These features make Firebase a powerful and user-friendly option for managing app versions and deployments.
Pricing Tiers
Firebase offers two pricing plans, catering to both beginners and advanced users:
- Spark Plan: This free plan is ideal for development. It includes 1 GB of Firestore storage, 5 GB of Cloud Storage, and 10 GB of Hosting storage at no cost. Remote Config is also available for unlimited daily active users without additional charges. However, exceeding the free quota disables the affected product for the rest of the month unless you upgrade.
- Blaze Plan: Designed for production apps, this pay-as-you-go plan provides access to premium Google Cloud services like Cloud Run and BigQuery. It includes a free tier, with usage-based fees beyond that – Cloud Storage costs $0.026 per GB after the initial 5 GB. Developers starting on the Blaze Plan can also claim $300 in Google Cloud credits to help offset initial costs.
Firebase’s pricing flexibility and robust features make it a versatile platform for developers at any stage.
sbb-itb-539ae66
6. Cloudinary
Cloudinary provides a streamlined solution for no-code developers looking to manage media assets effectively. By utilizing a “one file, many variations” approach, the platform minimizes storage needs by generating transformations from a single master file. Each file is assigned a version property like v1640995200, a UNIX timestamp that marks the exact moment it was last uploaded or updated. This timestamp is key for cache management, ensuring that users always access the most up-to-date versions of images or videos. This system forms the backbone of Cloudinary’s versioning capabilities.
Versioning Methods
Cloudinary’s versioning system includes an automatic backup feature, which is turned off by default but can be enabled in the Console Settings. Once activated, users can view, download, or restore older versions of files through the Media Library interface or the Admin API. Although Cloudinary keeps multiple versions internally, only the latest version is publicly accessible via standard delivery URLs. Adding the version timestamp to URLs bypasses browser and CDN caches, ensuring that updated content is delivered without delay. These tools integrate smoothly into no-code workflows, making version management effortless.
Integration Ease with No-Code Builders
Cloudinary offers two tools tailored for no-code users: MediaFlows for automating workflows and the Media Library Widget, which embeds a complete asset management interface into applications. These tools can be connected to platforms like Webflow using automation tools such as n8n, allowing users to perform tasks like uploading assets directly from URLs or updating metadata – all without writing a single line of code. The Upload Widget simplifies versioning and tagging, making it a perfect fit for no-code environments. While the Admin API is limited to 500 requests per hour on the Free plan, the Upload API supports unlimited requests.
Pricing Tiers
| Plan | Monthly Price | User Accounts | Monthly Credits | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 3 | 25 | Upload widget, API access, revision tracking, CDN delivery |
| Plus | $99 | 3 | 225 | S3 backup, auto-tagging, priority support |
| Advanced | $249 | 5 | 600 | Custom domain (CNAME), HTTPS SSL, authentication |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom | Custom | Multi-CDN support, SSO, enterprise-grade SLAs |
Backups stored in Cloudinary’s default location count toward the managed storage quota. However, paid plans offer the option to configure external storage solutions like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage, which do not impact Cloudinary storage limits. Usage is measured through a credit system that accounts for storage, bandwidth, and transformations.
7. Xano
Xano is all about backend versioning, keeping track of changes across databases, APIs, and functions. Its backend capabilities work hand-in-hand with the frontend versioning approaches we touched on earlier.
Versioning Methods
Xano uses a Schema Versioning system that logs changes with detailed timestamps, making it easy to visually compare past versions. It also tracks metadata – like input counts, functions, and results – for every version, which helps developers quickly identify the right version to restore if needed. And if something goes wrong? A single click can roll everything back to a previous state. For APIs, Xano supports manual versioning strategies, including URL paths (e.g., /v1/endpoint), headers, and parameters.
Integration Ease with No-Code Builders
Xano’s versioning features pair well with popular no-code platforms like Bubble, FlutterFlow, WeWeb, Bravo Studio, Adalo, and Draftbit, thanks to its REST API connectivity. Some tools, like Noloco, even use Xano’s metadata API to sync database schemas automatically – allowing tables and views to appear in the frontend almost instantly. Updates made in the frontend can sync back to the Xano database in under two minutes.
“With Xano, you can bypass hiring a developer; changes are yours to control.” – Chris Duncan, LEADstrike
Pricing Tiers
Xano offers flexible pricing options tailored to different development needs.
| Plan | Monthly Price | Version History | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | Not included | Database, API access, basic building tools |
| Launch | ~$29 | 3 most recent versions | Schema versioning, visual comparison tools, metadata tracking |
| Scale | Custom | 20 most recent versions | Extended version history, auto-scaling infrastructure |
| Enterprise | Custom | 20 most recent versions | SOC 2, HIPAA compliance, dedicated infrastructure |
The Launch plan is great for individual developers who need basic version control. Teams handling complex apps with frequent updates might find the Scale plan more suitable, offering extended version history and infrastructure built for scaling. According to Xano, this setup can lead to up to 3× faster development and 75% cost savings.
Feature Comparison Table
Picking the right tool boils down to your need for control, your comfort with technical setups, and how you envision your app evolving. Some tools offer built-in control, while others require external integrations to get the job done.
Here’s a quick breakdown of key metrics like versioning methods, ease of integration, pricing, scalability, and how well each tool suits no-code developers:
| Tool | Versioning Method | Integration Ease | Starting Price | Scalability | No-Code Ease |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AppInstitute | Native version tracking | High (DIY) | $49/month | Moderate | 5/5 |
| GitHub | Git-based (commits/tags) | Low (technical) | Free | High | 2/5 |
| Airtable | Revision history | High (native) | Free | Moderate | 5/5 |
| Supabase | Database/storage versioning | Moderate (API) | Free | High | 3/5 |
| Firebase | Storage versioning | Moderate (API) | Free | High | 3/5 |
| Cloudinary | Automatic/API versioning | Moderate (API) | Free | High | 3/5 |
| Xano | No-code backend versioning | High (native) | $29/month | High | 4/5 |
This table gives you a snapshot of what each tool offers, helping you make an informed choice before diving into implementation.
AppInstitute stands out for its no-code simplicity, making it perfect for business owners who want to create apps for iOS, Android, and PWA without writing a single line of code. GitHub, on the other hand, is ideal for developers who need powerful, Git-based version control but are comfortable with technical workflows. For apps heavy on media assets, Cloudinary offers smooth API-based versioning to manage updates efficiently. If you’re building an MVP with plans to scale rapidly, combining Xano or Supabase with a front-end builder can help you grow without the risk of being tied to a single vendor.
How to Implement Asset Versioning
To keep your app running smoothly, asset versioning is an essential practice. The process can be straightforward, especially with no-code tools that handle much of the work for you.
Start by using automatic versioning whenever possible. Tools like ImageKit can automatically create new versions when duplicate files are uploaded. With ImageKit, you can manage up to 100 versions per asset within your storage limits. This automation ensures efficiency while minimizing disruptions to your live environment.
In addition to automation, you should connect your codebase to a Git repository. This setup allows you to commit changes, merge branches, and create tagged releases. Instead of linking your application to a “latest” version – which could lead to unexpected issues – configure it to reference a specific tagged release. This approach gives you control over when updates are applied, reducing the risk of accidental changes affecting your users.
When working on updates, always create a new version before making changes to live applications. Many tools prevent editing of “Released” or “Production” versions to maintain stability. Use the “Create New Version” feature to work on a separate development copy, ensuring the live version remains unaffected during your updates.
Lastly, adopt semantic versioning (formatted as Major.Minor.Patch, such as 1.2.3) to clearly communicate the scope of updates. When you upload new media assets, clear your CDN cache to ensure users see the latest version right away. Adding descriptive tags like “Production Ready” or “Do Not Edit” can help streamline rollbacks and improve team collaboration.
Conclusion
Asset versioning plays a crucial role in keeping your no-code app stable and performing well. Without it, updates can disrupt live apps, leading to frustrated users and extended recovery times. The tools discussed in this guide provide a safety net, allowing you to test changes, undo errors, and maintain full control over your app’s assets.
When paired with the right tools, versioning becomes even more effective. AppInstitute’s built-in asset versioning, alongside tools for managing code, media, and backend systems, creates a reliable framework. This setup minimizes downtime and simplifies updates. With the ability to quickly revert to a previous version or pinpoint who made changes and when, you can focus on building the features your users need instead of spending hours troubleshooting.
Experienced no-code developers make versioning a core part of their workflow. They rely on semantic versioning, clear labeling, and automatic backups to scale efficiently. This strategy helps eliminate wasted time – an issue that can cost content teams over three weeks each year searching for the right files.
Choose tools that align with your specific needs, whether that’s compliance, seamless integration with your tech stack, or self-hosting options. By adopting strong versioning practices, you ensure your app remains dependable, while confidently rolling out updates.
FAQs
Why is asset versioning important in no-code app development?
Asset versioning plays a key role in no-code app development by keeping track of changes to visual and media assets like images, icons, and videos. With unique identifiers assigned to each version, it ensures a clear record of updates, avoids accidental overwrites, and makes it easy to roll back to previous versions if something goes wrong.
This is particularly important for no-code platforms, which are often used by non-technical creators. Asset versioning helps ensure apps are always using the right assets, supports a smooth user experience, and simplifies teamwork. With the help of versioning tools, creators can test and apply updates with confidence, safeguarding app performance and saving valuable time.
What are the benefits of using semantic versioning for app updates?
Semantic versioning provides a clear way to communicate the nature and impact of app updates. It follows a three-part system: major for updates that introduce breaking changes, minor for adding backward-compatible features, and patch for resolving bugs.
This approach helps developers, users, and tools handle updates efficiently, ensuring compatibility and reducing potential issues. Adopting semantic versioning creates a consistent and dependable update process that benefits everyone.
What should I look for in an asset versioning tool for no-code apps?
When choosing an asset versioning tool for no-code app development, it’s essential to start with integration capabilities. Make sure the tool integrates smoothly with source control systems. This allows you to track changes, manage branches, and revert to previous versions when needed. A seamless integration ensures your workflow stays efficient and reduces potential risks.
Another key factor is whether the tool supports automatic or manual versioning. Automatic versioning simplifies the process by creating a consistent audit trail, while manual options might require extra steps to implement changes. Ideally, look for tools that let you stage updates in a controlled environment before pushing them live. This helps maintain the stability of your production apps.
Lastly, evaluate the tool’s collaboration features. The best versioning tools enable multiple team members to work simultaneously without overwriting each other’s changes. Features like version naming, detailed version history, and update controls are invaluable for managing updates effectively while keeping the development process smooth and organized.
Related Blog Posts
- How to Build an App Without Coding Skills
- Top Cross-Platform Tools for Compatibility Solutions
- Cost Breakdown: Building Apps with No-Code Tools
- How No-Code Platform Pricing Works
Last Updated on January 6, 2026 by Becky Halls

0 thoughts on “Top Tools for Asset Versioning in No-Code Apps”