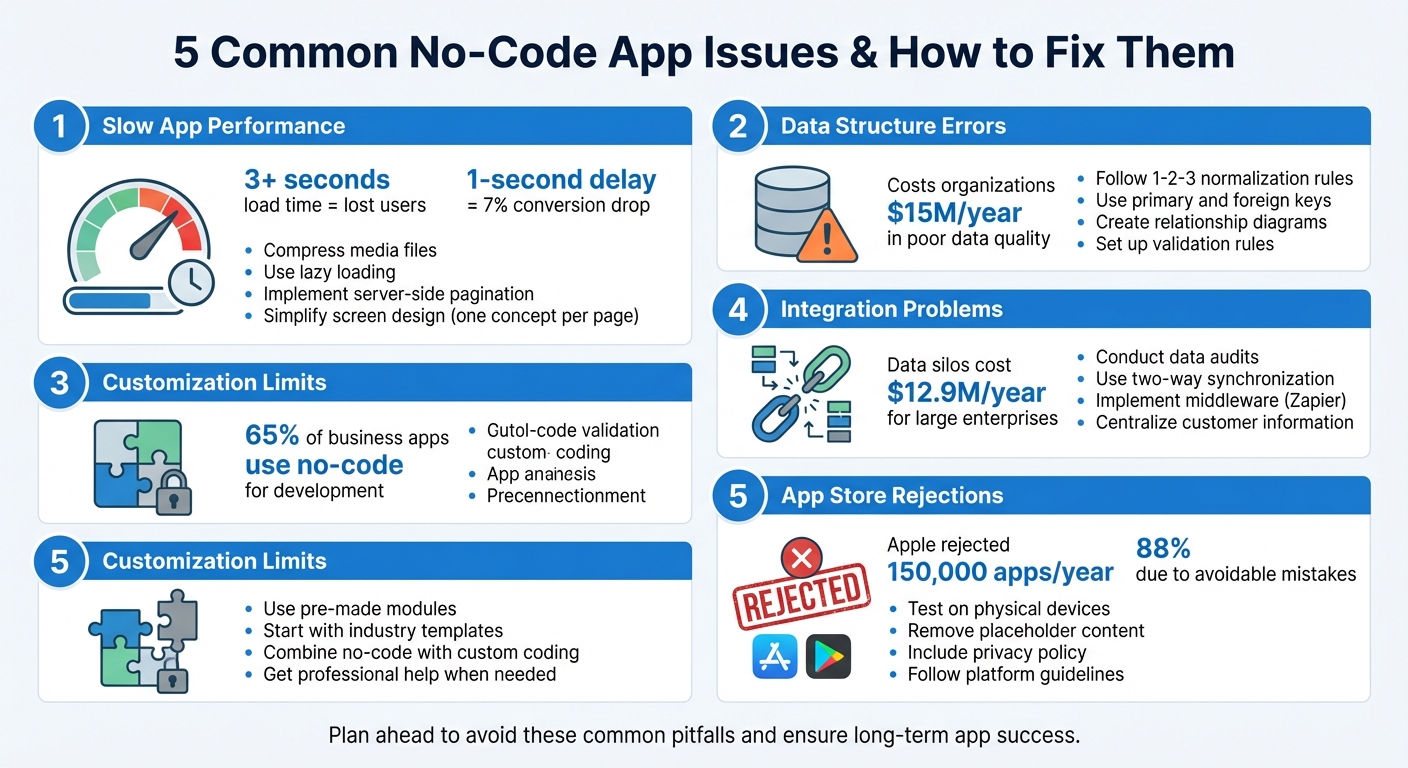
No-code platforms make app development faster and easier, but they come with challenges. From slow performance to app store rejections, these issues can derail your project. Here’s how to fix the five most common problems:
- Slow Performance: Compress media, simplify screens, and use lazy loading.
- Data Errors: Structure data properly with normalization rules to avoid redundancy.
- Customization Limits: Use pre-made modules or combine no-code with custom coding.
- Integration Problems: Audit data fields, use middleware like Zapier, and centralize information.
- App Store Rejections: Test thoroughly, follow guidelines, and remove placeholder content.
5 Common No-Code App Issues and Solutions
How to Solve NoCode App Performance Issues

Issue 1: Slow App Performance and Load Times
Few things drive users away faster than an app that drags its feet. If your mobile app takes over 3 seconds to load, you risk losing a large chunk of your audience. Even more alarming, a 1-second delay in page load can slash conversions by 7% and drop user satisfaction by 16%. For no-code apps, performance hiccups can appear unexpectedly, but the good news is they’re often fixable once you pinpoint the source of the problem.
What Causes Performance Problems
One of the most common culprits behind sluggish no-code apps is oversized media files. High-resolution images and uncompressed videos can dramatically slow things down. Another frequent issue stems from packing too many elements onto a single screen. Whether visible or hidden, all widgets load at once, creating unnecessary strain.
Inefficient data queries also play a big role in performance issues. Pulling an entire database instead of fetching smaller, targeted batches can bog down server performance. Poorly optimized code – like nested loops or redundant operations – only makes matters worse.
Third-party integrations, such as payment gateways or analytics tools, can quietly drag down performance if they aren’t optimized. Memory leaks are another sneaky problem: when an app doesn’t release memory after completing tasks, it starts consuming excessive RAM, leading to stutters, freezes, and even crashes.
Once you understand these root causes, you can take targeted steps to resolve them.
How to Fix Performance Issues
Begin by compressing your media files. Use lossy or lossless compression to reduce file sizes without compromising visible quality. For data-heavy apps, implement server-side pagination to load information in smaller, more manageable chunks, significantly cutting down load times.
Simplify your app’s design by adopting a “one concept per page” strategy. This means limiting the number of widgets and workflows on each screen. Additionally, enable lazy loading so non-essential content – like images further down a page – loads only when users scroll to it.
Shift resource-heavy computations from the client side to the server. This is especially helpful for users with older devices, as it ensures smoother performance. Finally, take advantage of caching to reduce repeated server requests.
| Performance Issue | Common Cause | Recommended Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Screen Loads | Too many widgets/elements | Limit widgets; use separate pages |
| Delayed Content | Large uncompressed media | Use compression; implement lazy loading |
| Data Fetching Lag | Inefficient queries | Add indexes; use server-side pagination |
| Freezing | Memory leaks | Profile and release unused objects |
AppInstitute’s platform offers built-in tools to help you optimize performance across iOS, Android, and Progressive Web Apps. The drag-and-drop editor makes it simple to organize screens efficiently without overloading any single page.
When to Get Professional Help
If you’ve already compressed media, implemented pagination, and streamlined your layouts but still experience lag, it might be time to bring in an expert. Professional guidance becomes critical when scaling to accommodate thousands of users or resolving complex database issues that go beyond basic fixes.
AppInstitute provides 1-to-1 consultations with app development experts to help you fine-tune your app’s architecture and choose the right features from the start. For more advanced performance challenges, their Hire A Pro service connects you with professional developers who can tackle tough problems. Getting expert advice early can save you from creating inefficiencies that are harder to fix later.
Issue 2: Data Structure Errors and Logic Problems
When data is poorly organized, it creates a ripple effect of problems – ranging from inconsistent records to unpredictable app behavior. If your data isn’t structured correctly from the beginning, you’ll likely encounter duplicate entries, conflicting records, and sudden functionality breakdowns. According to industry research, these issues cost organizations an average of $15 million per year.
The trouble often starts small. You might add a few extra fields without considering how they connect, or accidentally delete critical information when removing a single entry. Things get even messier when the same data exists in multiple places, and you update one copy but forget the others. This kind of disorganization can render your entire database unreliable. Let’s break down the common mistakes that lead to such chaos.
Typical Data Structure Mistakes
One of the most damaging errors is data redundancy – storing the same information in multiple tables. For instance, instead of linking to an employee ID, you might repeatedly store employee names in every order record. This creates inconsistencies when an employee’s details change. These inconsistencies lead to three types of database anomalies that can disrupt your app:
- Insert anomalies: You can’t add new records without including unnecessary or incomplete information.
- Delete anomalies: Deleting one record unintentionally removes unrelated but vital data.
- Update anomalies: Duplicate data across the database means updating one instance while missing others, resulting in conflicting records.
Another frequent mistake is cramming multiple values into a single field, which violates basic data organization principles. Many no-code builders also skip mapping relationships between entities like “Customers”, “Products”, and “Orders” before starting. This oversight often leads to redundant entries and manual errors. Adding fields without a clear schema further bloats databases, making them slow and harder to manage as they grow.
These examples underscore the importance of well-thought-out data modeling.
How to Build Better Data Models
To organize your data effectively, follow the 1-2-3 Rule of Normalization:
- Ensure every column contains a single, indivisible value without repeating fields.
- Move columns that depend only on part of a composite key into separate tables.
- Eliminate redundant data by removing columns that rely on non-key fields.
| Normal Form | Goal | No-Code Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1NF | Eliminate repeating groups | Use linked tables for repeating data. |
| 2NF | Remove partial dependencies | Separate data that relates to only part of a composite key. |
| 3NF | Remove transitive dependencies | Move helper details (e.g., Department Name) to a table linked by a Department ID. |
Create relationship diagrams to visualize how your entities connect. Use Primary Keys to uniquely identify each record and Foreign Keys to link related tables. This approach minimizes redundancy and ensures data integrity.
For U.S. businesses, AppInstitute offers industry-specific templates tailored for sectors like restaurants and retail. These templates come with pre-configured data structures that follow best practices, saving you the hassle of building from scratch. The platform also includes Data Forms to simplify tasks like gathering customer feedback or RSVPs without needing to design a schema manually.
To avoid “dirty data”, set up validation rules for formats like dates, phone numbers, and emails. This prevents invalid entries from cluttering your system. Gartner has noted that poor data quality compromises digital initiatives and erodes customer trust.
Testing and Updating Data Models
Once you’ve restructured your data, the next step is to test its integrity. Always test changes in a cloned or dedicated test environment first. This ensures your production data remains safe while giving you a controlled space to identify and fix logic errors.
Run simulations with test records to confirm that your model aligns with business requirements. For example, query all orders for a specific product to verify that relationships between entities work as intended. If you’re planning significant updates, simulate data processing at three times your anticipated annual volume to ensure the system can handle stress.
AppInstitute offers a 30-day free trial where you can build and test your app, including sending push notifications, before going live. This gives you plenty of time to fine-tune your data structure without risking disruptions to your production environment. For apps with complex data models or custom functionality, experts recommend budgeting around $4,000 for professional development support.
Issue 3: Customization Limits and Missing Features
No-code platforms now drive over 65% of all business applications in development. They’re a game-changer for speed and simplicity, but they do come with limitations. Imagine wanting a sleek, personalized interface with unique animations, only to realize your platform locks you into rigid templates. Or maybe you need complex business logic that goes beyond what drag-and-drop tools can handle.
These platforms often prioritize ease of use over flexibility, which can lead to compromises. Many include generic, one-size-fits-all components that might slow down your application or limit its potential.
Understanding Platform Restrictions
The constraints of no-code platforms generally fall into three main categories:
- Design limitations: Predefined templates can restrict creative freedom, making it harder to maintain a unique brand identity.
- Functional barriers: Advanced workflows or custom data processing might be out of reach.
- Integration challenges: Limited pre-built connectors can make syncing with specialized software difficult.
Take “custom states”, for example – temporary variables that enable dynamic features like toggling dark mode. These often require a more technical approach than drag-and-drop tools can provide. Another issue is vendor lock-in, where proprietary ecosystems make it tough – or even impossible – to export your source code or migrate your app without starting from scratch. These challenges highlight the need for practical solutions.
Working Within Platform Limits
Understanding these constraints can help you make the most of what’s available. Before jumping to custom development, explore whether the platform’s built-in features can meet your needs. For instance, AppInstitute offers pre-made modules like loyalty cards, online ordering, push notifications, and CRM tools. These allow small businesses to achieve tailored functionality without diving into coding.
A coffee shop, for example, could use a stamp-based loyalty program to encourage repeat visits, while a salon might utilize integrated booking forms to streamline appointments – all without writing a single line of code.
“AppInstitute was founded on the belief that small businesses should have the same mobile capabilities as big brands without hiring a developer.” – Ian Naylor, Founder, AppInstitute
Starting with industry-specific templates can also save time and reduce the need for custom solutions. A free one-on-one consultation with app development experts can help identify ways to adapt existing tools to your business needs. By defining your app’s purpose and core features upfront, you can choose a platform that aligns with your goals and minimizes the need for workarounds.
When Custom Development Is Needed
Sometimes, platform limitations can only be resolved through professional development. If your app requires advanced features, complex data models, or real-time updates that no-code tools can’t handle, a hybrid approach might be the answer. Combining no-code for the basics with custom coding for advanced needs gives you flexibility without unnecessary costs.
AppInstitute’s Hire A Pro service starts at $499, offering professional custom app development for users who need features beyond standard platform capabilities. Considering that development costs range from $5,000 for simple apps to over $300,000 for highly advanced solutions, targeted professional help can be a smart investment. Before diving into custom development, confirm that your platform supports advanced integrations and allows for data portability and code export. These factors can save you headaches – and expenses – down the road.
sbb-itb-539ae66
Issue 4: Integration Problems and Disconnected Data
Imagine this: customer data is stored in your app, sales records are locked in your CRM, and order history is stuck in your payment processor. These isolated data silos cost businesses an average of $12.9 million per year. For example, a customer updates their email in your app, but your marketing team keeps reaching out to the outdated address because the systems aren’t communicating. This kind of fragmentation disrupts workflows and sets the stage for integration failures.
Common Integration Failures
Integration issues often arise from API restrictions and complex authentication protocols. Some systems enforce strict rate limits on data requests, while others require multi-layered OAuth tokens that expire unexpectedly. Then there’s the problem of mismatched data – your app might label a field as “customer_name”, but your CRM calls it “contact_full_name”, leading to failed transfers or corrupted data.
One-way syncs add to the chaos, creating convoluted workflows that risk infinite loops and data corruption. Legacy systems bring their own headaches, often using outdated, proprietary formats that modern no-code platforms struggle to process. And when a single link in your integration chain fails – like a third-party API changing without notice – the entire workflow can grind to a halt.
How to Integrate Systems Properly
To tackle these challenges, start with a data audit before connecting systems. Map out fields across platforms and create a clear plan to handle mismatches. Opt for two-way synchronization to ensure consistency – bidirectional connections keep all tools in sync without needing constant manual updates.
AppInstitute simplifies this process with its user management and data forms, which centralize customer information directly within your app. This eliminates the need for juggling multiple external integrations. Instead of syncing data across several platforms, you can collect and store it in one unified location. Middleware tools like Zapier, which connects over 8,000 apps, can also fill gaps where native integrations are missing. To avoid performance slowdowns, schedule syncs during off-peak hours and use caching to reduce API calls.
Reducing Data Fragmentation with AppInstitute
AppInstitute’s built-in tools are designed to prevent data fragmentation altogether. The platform’s ordering features and user management tools keep customer data consistent and organized within your app. Whether a customer places an order, updates their profile, or redeems a loyalty reward, all that information stays in one cohesive system instead of scattering across disconnected platforms.
The Message Centre further simplifies things by consolidating all customer communications in one place. By unifying your systems, your app delivers the seamless experience discussed earlier. And for businesses requiring external integrations, AppInstitute offers submission support services to help navigate the technical steps of launching your app on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
Issue 5: App Store Submission and Rejection Problems
You’ve poured your time and effort into building and testing your app, and you’re ready to share it with the world. Then comes the dreaded rejection notice from Apple or Google. It’s a common scenario – Apple alone rejected 150,000 apps in a single year, with around 88% of those rejections stemming from avoidable mistakes. Once you’ve tackled integration issues, navigating app store guidelines becomes the next big challenge. The upside? Most submission problems are predictable, and understanding what causes rejections can help you sidestep weeks of headaches.
Why Apps Get Rejected
The most frequent culprit behind app rejections is technical failure. Apps that crash during review, have bugs, broken links, or other glaring issues are flagged immediately. Apple’s Guideline 2.1 states it clearly: “We will reject incomplete app bundles and binaries that crash or exhibit obvious technical problems”.
Another common stumbling block is the “minimum functionality” requirement. If your app functions like a simple website wrapper – essentially mimicking a mobile browsing experience – it’s likely to be rejected under Guideline 4.2. Apple often provides feedback like: “Your app provides a limited user experience as it is not sufficiently different from a mobile browsing experience”. To avoid this, your app must utilize native features like push notifications, GPS, or the camera.
Metadata errors are another frequent issue. Submissions with incomplete or incorrect descriptions, or those that mention competing platforms (e.g., referencing “Android” in an iOS app submission), are likely to be rejected. Even a single placeholder text, like “Lorem Ipsum”, can lead to rejection, as it signals an unfinished product. In fact, over 40% of unresolved submission problems fall under Guideline 2.1, which covers crashes, placeholder content, and incomplete information.
Privacy and legal compliance are equally critical. Missing privacy policies, lack of in-app account deletion options, or improper data handling can result in rejection. Apple mandates: “All apps must include a link to their privacy policy in the App Store Connect metadata field and within the app in an easily accessible manner”. Additionally, using third-party processors for digital content instead of Apple’s In-App Purchase system is another common pitfall.
Pre-Submission Checklist
Before submitting your app, it’s crucial to test it on multiple physical devices – not just emulators. Tools like TestFlight can help you catch device-specific issues. Double-check all links, including your support URL and privacy policy, which must appear in both your App Store Connect metadata and within your app settings. If your app requires a login, provide a working demo account (with username and password) in the “App Review Information” section so reviewers can fully test its features.
Make sure to remove all placeholder content, dummy images, and labels like “Beta” or “Alpha.” Keep your app name and subtitle under 30 characters. Screenshots should showcase the app in use, not just logos or promotional graphics. For iOS submissions, scrub any references to Android, Google Play, or similar competitors from your descriptions and screenshots.
Plan to submit your app at least a week before your intended launch date. While Apple’s review process often wraps up within one to five days, it can take up to two weeks.
AppInstitute’s Submission Support Service
Once you’ve checked all the boxes, AppInstitute’s Submission Support Service can take the stress out of the process. Their team handles the technical aspects of submitting your app to both the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. They ensure your app complies with all regulations, making it launch-ready.
“Alternatively, if you prefer, we can submit your iOS App to the App Store for review for you, and we’ll be happy to work with you to guarantee your App is accepted.”
This service includes responding to feedback from app store reviewers and addressing any technical or content-related objections on your behalf. AppInstitute’s platform also simplifies compliance by integrating native features like location services and calling, which are often required for approval. They even assist with completing the “Publish Page”, ensuring you meet requirements like content ratings and age ranges for apps targeting specific audiences.
With app reviews now completed within 24 hours for 90% of submissions, AppInstitute’s service ensures quick responses to feedback, keeping your launch timeline intact. Starting at $39/month with a 30-day free trial, their submission service offers an efficient way to get your app live without the hassle of navigating complex guidelines.
Conclusion
Creating a no-code app comes with its share of technical hurdles, but with careful planning and the right strategies, these challenges can be tackled effectively. The issues we’ve discussed – like slow performance, data structure mishaps, customization limits, integration headaches, and app store rejections – are all manageable when approached thoughtfully. The key? Planning ahead to sidestep problems before they arise.
By strategically designing your app, you can ensure long-term stability and scalability. Start with a well-structured data model to reduce redundancy and speed up queries. Regular testing is essential to catch potential issues early, helping you avoid common pitfalls. Take advantage of your platform’s built-in tools – like lazy loading, server-side pagination, and batch operations – to improve performance. These optimizations not only make your app run smoother but also position your business for greater success.
For U.S. businesses eyeing the nearly $45 billion mobile app market, platforms like AppInstitute offer a streamlined way to build professional-grade apps. With integrated business modules and tools to simplify app store submissions, AppInstitute makes it easier to get your app live – often within a week. Starting at $49 per month with a free trial available, it’s a practical solution to launch a high-quality app without breaking the bank.
No-code development is reshaping the way businesses approach app creation, emphasizing speed and control over traditional methods. With 62% of businesses now building mobile apps, the question isn’t whether you should create one – it’s how to do it right.
FAQs
What are the best ways to improve the performance of my no-code app?
To get the best performance out of your no-code app, start by fine-tuning your data structure. Cut down on redundant data, use indexes for fields that are frequently queried, and implement techniques like pagination or lazy loading. These steps ensure your app only loads the data it needs, which can make a big difference in response times – especially as your user base grows.
Keep an eye on your app’s performance in real-time by tracking key metrics such as API response times, error rates, and page load speeds. Setting up alerts can help you catch issues before they escalate. On the client side, streamline your app’s interface by reducing the number of widgets or components, caching commonly used data, and offloading heavy calculations to the server or background processes. For calls to external services, using asynchronous methods can also keep your app’s user interface responsive and smooth.
When it comes to database queries, focus on efficiency. Filter data to retrieve only what’s necessary, limit the columns you pull, and take advantage of query caching if it’s available. Regular load testing is another essential step – it helps pinpoint bottlenecks so you can adjust server resources or upgrade your hosting plan as needed. By putting these practices into action, your app will be well-equipped to handle growth and deliver a seamless experience for users across the United States.
What are the most common data structure mistakes in no-code apps, and how can I avoid them?
One mistake often seen in no-code apps is relying on a single, flat table to store all kinds of data – like users, orders, and products – rather than setting up separate tables with defined relationships. This approach can lead to challenges with filtering, reporting, and scaling. To steer clear of these issues, create distinct tables and use foreign keys to link them effectively.
Another common pitfall is neglecting data normalization, which results in storing the same information in multiple places. This redundancy not only wastes storage but also slows down performance and makes updates prone to errors. A better approach is to structure your data in a way that reduces duplication, ensuring it remains efficient and scalable.
Lastly, performance can take a hit when field types are inconsistent or when large datasets are loaded without using pagination. Always assign the appropriate data types – like dates or numbers – and implement pagination when dealing with extensive data sets to keep things running smoothly. Platforms like AppInstitute make these tasks easier by offering tools to define relationships, set proper field types, and optimize data structures, empowering you to create professional, efficient apps.
When should I switch from a no-code app to custom development?
When your app’s requirements outgrow the capabilities of a no-code platform, it might be time to explore custom development. This shift often becomes necessary when you encounter performance bottlenecks as your user base expands, face limitations in implementing unique features like intricate workflows or specialized compliance tools, or run into integration roadblocks with third-party services or APIs that aren’t supported by the platform.
Other red flags include escalating costs tied to usage-based pricing, the need for stronger security measures to meet regulatory requirements, or challenges in adapting the app to keep up with future growth. No-code platforms – like AppInstitute – are fantastic for quickly building and launching apps, but when scalability, flexibility, or long-term cost management takes center stage, custom development is often the smarter choice.
Related Blog Posts
- How to Build an App Without Coding Skills
- Small Business App Development: Complete Guide
- Common Integration Issues in No-Code Platforms
- Cost Breakdown: Building Apps with No-Code Tools
Last Updated on December 31, 2025 by Becky Halls
0 thoughts on “5 Common No-Code App Issues Solved”